Penetrant testing principle and advantages
›Penetrant Testing is one of the effective method for detecting surface flaws,.
›It can be used on Metals, non-metals, plastics, ceramics & Glass.
›Not suitable for Porous materials such as wood, bricks, concrete, & other non graded castings, sponge
Qualification of Examination Personel
- ›Able to read a Jaeger Type No. 2 Standard Chart at a distance of not less than 12 in. (300 mm),
- ›Should be capable of distinguishing and differentiating contrast between colors used.
- ›These requirements shall be checked annually.
- ›Should clear the Examinations with percentage stated in ASNT SNT-TC-1A
Basic Principle
›Capillary Action
– Low surface tension fluid( dye) penetrates in to clean and dry defects open to the surface.
Advantages of PT
- ›High sensitivity to small surface discontinuities.
- ›Vast application -metallic and nonmetallic, magnetic and nonmagnetic, and conductive and nonconductive materials may be inspected.
- ›Large areas and large volumes of parts/materials can be inspected rapidly and at low cost.
- ›Parts with complex geometric shapes are routinely inspected.
- ›Indications are produced directly on the surface of the part and constitute a visual representation of the flaw.
- ›Aerosol spray cans make penetrant materials very portable.
- Penetrant materials and associated equipment are relatively inexpensive.
Disadvantages of PT
- ›Only surface breaking defects can be detected.
- ›Only materials with a relatively nonporous surface can be inspected.
- ›Pre-cleaning is critical since contaminants can mask defects.
- ›Metal smearing from machining, grinding, and grit or vapor blasting must be removed prior to LPI.
- ›The inspector must have direct access to the surface being inspected.
- ›Surface finish and roughness can affect inspection sensitivity.
- ›Multiple process operations must be performed and controlled.
- ›Post cleaning of acceptable parts or materials is required.
- Chemical handling and proper disposal is required.
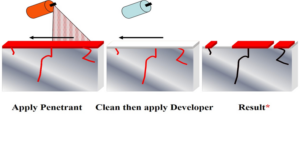
General Steps:
- Pre- Cleaning
- Apply Penetrant
- Dwell Time
- Excess Penetrant Removal
- Apply Developer
- Developing time
- Indications
- Interpretation
- Report
- Post Cleaning
For any further information about Non Destructive testing , for material testing service, third party inspection service or training and certification for Non Destructive Testing Methods visit https://aqcinspection.com/
Visit our technical and career updates at our Blog site https://advancedqualitycentre.blogspot.com . https://ndtcenter.blogspot.com our website https://aqcinspection.com/news-events/ for many more blogs to learn more.


Comments
Post a Comment