Radiation Protection
Radiation Protection and Safety measures
Radiation Safety
Radiation we are discussing here are high frequency electromagnetic radiations.
Examples of Electromagnetic radiations are: Light, heat, Radio waves, Infrared, ultraviolet, Xray & Gamma Rays, though light . X ray both are electromagnetic radiations. X ray is considered hazardous, as it is of very high frequency.
- Radiation workers in India is protected AERB (Atomic Energy Regulatory Board)
- The mission of the AERB is to ensure the use of ionizing radiation and nuclear energy in India does not cause undue risk to the health of people and the environment.
- Under AERB -RSD (Radiological Safety divisions) governs the safety requirements of radiation workers.

Activities of AERB
- Frames regulations and amends rules
- Directs BARC(BABA ATOMIC RESEARCH CENTRE)to implement the regulations
- Publication of codes and standards
Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) in US
International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP)
Units of Radiation dose measurement
- The Roentgen is a unit which expresses radiation protection exposure and is based on the “ionising” effect of radiation.
- “Ionisation” creates an ion pair which consists of positively charged particle and negatively charged particle.
- The number of ion pairs can be measured by the amount of electric current they produce, the electric current can in turn activate a survey meter.
Units of DOSE rate:
RAD- Radiation Absorption Dose
RBE- Radiation Biological Effect
REM- Radiation Equivalent Men
- RAD- Radiation absorption Dose
- Grey – Gy
Radiation absorbed by a nonliving cell
100 rad = 1 Gy
Equivalent Dose
Radiation absorbed by a living cell
- REM – Roentgen Equivalent Men
- Sievert – Sv
100 rem= 1 Sv
Regulatory Limits for Occupational Exposure
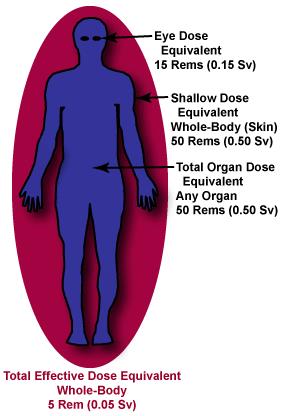
- Body cells which are active in dividing and reproducing are most vulnerable to radiation damage
- For Persons under 18 year old the limits are only 10% (0.5 REMS) of the given value
- Females of child bearing age are allowed to receive less mR than the radiation workers,
- For Pregnant women – not more than 0.5 REMS for the total gestation period.
- For a non radiation worker/Public – 0.1 REMS/year.
Effect of whole body dosage within 24 hour period
| Whole body dose | Effects |
| 0 to 25 REMS | No detectable Effect |
| 25 to 50 REMS | Slight Temporary Blood Changes |
| 100 REMS | Nausea, Fatigue |
| 200 to 250 REMS | First Death |
| 500 REMS | Half Die (median lethal dose) |
RESPECT BUT DO NOT FEAR RADIATION
Radiation Detection and Measurement devices
- Survey meters
- Direct Read Pocket Dosimeter
- Digital Electronic Dosimeter
- Audible Alarm Rate Meter
- Film Batches
- Thermoluminescent Dosimeter
- Lead Aprons
- Lead Suit

To learn more on NDT training, NDT courses and Training Institute for specific ndt methods, feel free to contact us at https://aqcinspection.com/training/ and for services on radiography testing services and other NDT services and Mechanical testing services contact us.
Visit our technical and career updates at our Blog site https://advancedqualitycentre.blogspot.com . https://ndtcenter.blogspot.com our website https://aqcinspection.com/news-events/ for many more blogs

Comments
Post a Comment