Preheating in Welding Procedure Specification
Preheating in Welding Procedure Specification:
Preheating is the act of heating the base metal before starting to weld. It is considered very essential in high thickness materials, Cr-Mo Steels & HSLA High Speed Low Alloy steels, etc…
Here we are going to answer the below topics
- What is Preheating ?
- Why is Preheat Essential ?
- What is difference between Preheat, interpass temperature and Post weld heat treatment?
- How to calculate Pre-Heat Temprature ?
- Where to Preheat in the material ?
- What is the requirement of pre heat given in International Standards ?
What is Preheating ?
It involves heating the base metal to a minimum required temperature before start of the weld. The heat should be maintained until the welding is finished.
As per AWS D1.1 Preheat is defined as:
The temperature of base metal in the volume surrounding the point of welding, immediately before the welding is started. In a multi-pass weld, it is also the temperature immediately before the second and subsequent passes are started.
What is difference between Pre-heat, Interpass & Post weld Temprature ?
Preheat is specified Minimum Temperature that should be available in the base metal before welding.
Generally pre-heat is applied up to 1 hour before the welding to ensure even temperature throughout the welding area. The minimum temperature to be ensured just before the commencement of weld.
Inter-pass Temperature is specified as Maximum Temperature allowed in the base metal and weld metal before commencement of next weld pass.
Post Heat is applied for the purpose of hydrogen release. After completing the weld, it is recommended to apply Post heat temperature before the weld metal cools to room temperature.
Why is Pre Heat Required ?
- Pre heat slows down the cooling rate of weld metal, Heat Affected Zone (HAZ), and adjacent base metals,
- Preheating produces good Microstructure
- Preheating avoids martensitic formation in the metal grain structure & prevents brittleness
- Preheating removes diffusable hydrogen in base metal and avoids Hydrogen Induced Cracking (HIC)
- Burns unwanted impurities in the base metal before welding
- Reduces expansion and contraction rate
- Improves mechanical properties
How to find preheating Temperature ?
Pre-heating temperature requirements are given in Standards / Codes, few of the examples of the standards are given below:
An example of preheat temperature as per code is given below
| S.No | Code | Where to Refer |
| 1 | ASME ection VIII | Anon mandatory Appendix R |
| 2 | AWS D1.1 , Structural Steel Welding Code | Table 3.3 |
| 3 | ASME B31.1, Power Piping code | Table 331.4.1 |
| 4 | ASME B31.3, Proces Piping code | Table 330.1.1 |
Requirements of Pre-Heating as per ASME B31.1
For Carbon Steel with P No.1 – If Base metal Thickness T≤ 25mm & C% >.30 → 10⁰C (minimum)
- If Base metal Thickness T>25mm & C%≤ .30 → 10⁰ C (minimum)
- If Base metal Thickness T>25mm & C>0.30 → 95⁰ C (minimum)
For Metals of other P Number the requirements are obtained from the referencing code as shown above
Where to Pre Heat the Joint prepared for Welding ?
Pre heat the material . Not only in the weldable location also the nearby areas of weld axis , to atleast 3’’ on both sides of the axis as shown below
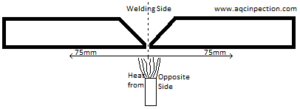
Methods of Preheating
Flame Heating , Induction Heating & Resistance Heating
To know more about other heating requirements such as Inter-pass temperature, post weld heat treatment and type of PWHT, keep in touch by liking and following the blog pages and FB pages,
For more details about , welding procedure specification, welding training, welder qualification and welding inpections , reach us at 04224342244, 9489342244 or visit https://aqcinpection.com/
Visit our technical and career updates at our Blog site https://advancedqualitycentre.blogspot.com . https://ndtcenter.blogspot.com our website https://aqcinspection.com/news-events/ for many more blogs to learn more.


Comments
Post a Comment